铝挤成型是一种加工方式,用于将铝合金制成具有明确横截面轮廓的物体,用于许多不同类型的用途。铝挤成型工艺充分利用了铝独特的物理特性组合。它的延展性使其易于加工和铸造,但铝的密度和刚度是钢的三分之一,因此所得产品具有强度和稳定性,尤其是在与其他金属合金化时。
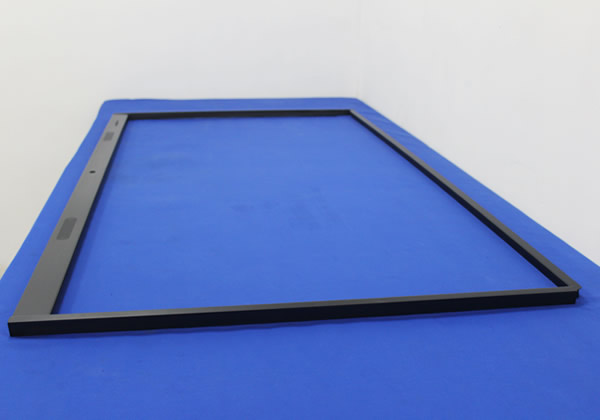
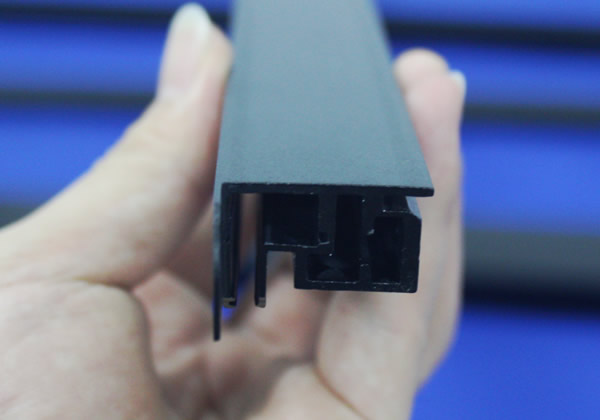



铝挤成型的过程包括以下步骤:
▶ 在完成模具的设计和创建形状时,将铝合金的圆柱形胚料加热到800°F-925°F。
▶将铝胚放入加载机中,在那里添加润滑剂以防止其粘在挤出机、柱塞和手柄上。
▶ 使用柱塞将巨大的压力施加到虚拟块上,该虚拟块将铝坯推入容器中,迫使其通过模具
▶ 为了避免氧化物的形成,使用液态或气态的氮气,并允许氮气流过模具的各个部分。这会产生惰性气氛并延长模具的使用寿命。
▶ 挤出的零件作为一个细长的部件进入跳动台,该部件现在与模具开口的形状相同。然后,它被拉到冷却台上,在那里风扇冷却新创建的铝挤压件。
▶ 冷却完成后,将挤压好的铝移至担架上,进行拧紧和加工硬化。
▶ 淬硬的挤压件被带到锯台上,并根据所需的长度进行切割。
▶ 最后一步是在陈酿炉中加热处理挤压件,通过加速老化过程使铝硬化。